Milia, commonly referred to as eyelid bumps, are small, benign cysts that can appear on various parts of the face, including the eyelids. While they are generally harmless, understanding their nature, causes, types, and management options is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
Causes of Milia:
Milia form when keratin, a protein present in the skin, gets trapped beneath the surface. Several factors contribute to this process:
- Skin Trauma: Injuries, burns, or excessive exfoliation can damage the skin, leading to milia formation.
- Clogged Pores: Accumulation of dead skin cells or oil can block the pores, trapping keratin beneath the surface.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may inherit a tendency to develop milia from their family members.
- Skin Conditions: Conditions like eczema or psoriasis, which affect the skin’s barrier function, can increase the likelihood of milia.
- Use of Heavy Skincare Products: Creams and ointments that are too thick or occlusive can clog pores and contribute to milia development.
Types of Milia:
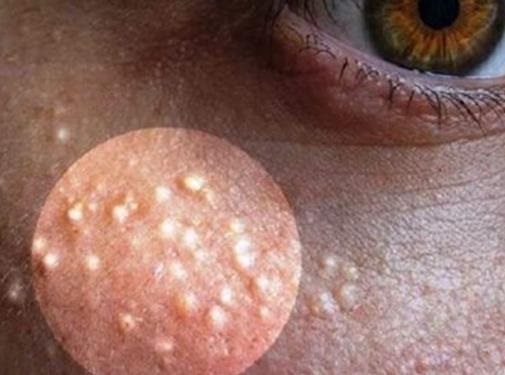
Understanding the different types of milia can help in identifying and treating them:
- Primary Milia: These are common and appear spontaneously. They are typically found on the face, particularly around the eyes, nose, and cheeks. Primary milia are often seen in newborns and can occur in adults as well.
- Secondary Milia: These develop as a result of skin damage or conditions such as sun damage, burns, or certain dermatological treatments. Secondary milia can also occur after the use of topical corticosteroids.
- Milia En Plaque: A less common type that appears as a larger, elevated plaque rather than individual bumps. It is often associated with systemic diseases or severe skin conditions.
- Pachydermoperiostosis: This rare condition, also known as “primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy,” involves thickened skin and bone abnormalities. Milia in this context can be part of a broader clinical picture.
Risk Factors for Developing Milia:
Several factors can increase the risk of developing milia:
- Age: Infants are particularly prone to milia due to their delicate skin, but adults can also develop these bumps.
- Skin Type: Oily and combination skin types are more susceptible due to the increased likelihood of clogged pores.
- Environmental Factors: Excessive sun exposure can damage the skin and promote milia formation.
- Medical Treatments: Prolonged use of topical steroids or other occlusive treatments can contribute to milia.
- Genetics: Family history of milia can predispose individuals to developing them.
Read: Fintechzoom How Much House Can I Afford – A Comprehensive Guide!
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Milia:
Milia are characterized by the following symptoms:
- Appearance: Small, white, or yellowish bumps on the skin, typically less than 2-3 millimeters in diameter.
- Location: Commonly found on the face, especially around the eyes and cheeks, but can also appear on other parts of the body.
- No Associated Pain: Milia are usually asymptomatic and do not cause itching or pain.
- Diagnosis is typically straightforward and involves:
- Clinical Examination: A dermatologist can often diagnose milia through a visual inspection of the skin.
- Histological Examination: In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and differentiate milia from other skin conditions.
Treatment Options for Milia:
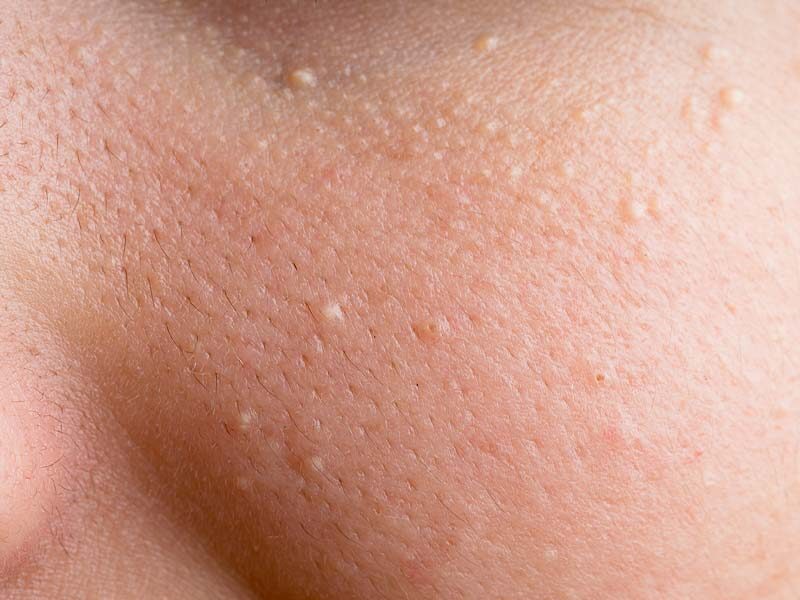
While milia often resolve on their own, treatment options are available for those seeking removal:
- Topical Retinoids: Products containing retinoids, like tretinoin, can help by promoting skin cell turnover and preventing keratin buildup.
- Chemical Peels: Peels containing glycolic acid or salicylic acid can exfoliate the skin and help remove milia.
- Cryotherapy: Involves freezing the milia with liquid nitrogen, which can be effective in removing them.
- Laser Therapy: Lasers can target and destroy the cysts without damaging surrounding skin.
- Manual Extraction: A dermatologist can use a sterile needle or comedone extractor to remove milia.
Read: Hasan Minhaj Net Worth – From Stand-Up Star to TV Icon!
Home Remedies for Removing Milia:
For those preferring home treatments, several remedies may help:
- Exfoliation: Regularly using a gentle exfoliating product can help prevent dead skin cells from accumulating.
- Steam Treatments: Steaming the face can help open pores and facilitate the release of trapped keratin.
- Natural Oils: Oils like coconut oil, tea tree oil, or jojoba oil have antibacterial and moisturizing properties that may help reduce milia.
- AHA Products: Products containing alpha-hydroxy acids can help in exfoliating the skin and preventing milia formation.
Prevention Tips for Milia:
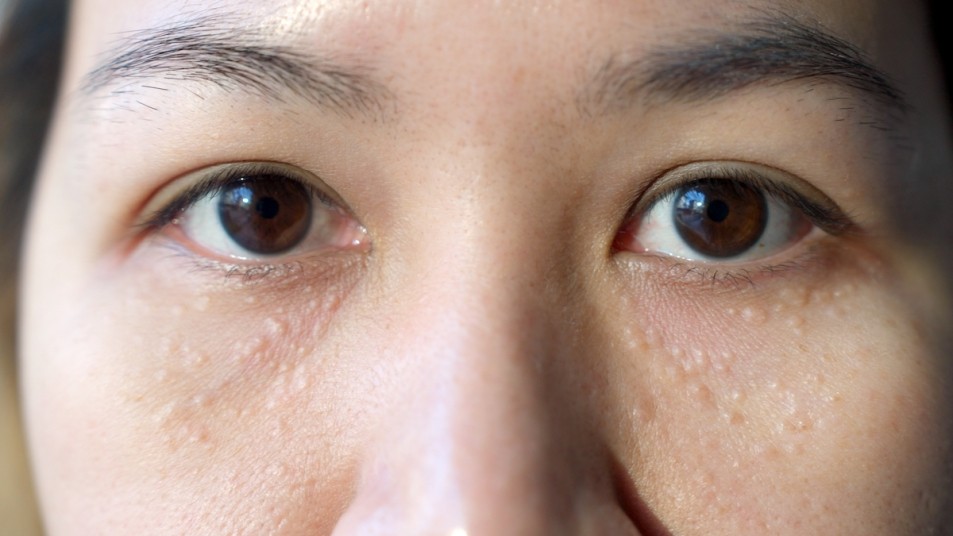
To reduce the risk of developing milia, consider these preventive measures:
- Sun Protection: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher to protect the skin from UV damage.
- Routine Skincare: Use a gentle cleanser and exfoliate regularly to maintain clear pores.
- Avoid Heavy Creams: Opt for non-comedogenic and lightweight skincare products to minimize pore clogging.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet to support overall skin health.
When to See a Doctor for Milia:
While milia are generally benign, seek medical advice if:
- Persistent Bumps: If milia do not resolve on their own or continue to appear despite treatment.
- Changes in Appearance: If the bumps change in color, size, or shape, which might indicate a different condition.
- Discomfort: If you experience pain, redness, or swelling in the affected area.
FAQ’s:
1. What are milia?
Milia are small, white bumps on the skin caused by trapped keratin beneath the surface. They are generally harmless and often found on the face.
2. Are milia the same as pimples?
No, milia are different from pimples. Pimples are inflamed blemishes caused by acne, whereas milia are non-inflammatory cysts resulting from trapped skin cells.
3. Can milia be removed at home?
Mild home remedies, such as exfoliation and steaming, can help manage milia, but persistent cases should be evaluated by a dermatologist.
4. Is it safe to use retinoids for treating milia?
Topical retinoids can be effective for treating milia by promoting skin cell turnover. Consult a dermatologist before using them to ensure they are suitable for your skin type.
5. How can I prevent milia?
Prevent milia by using sunscreen, maintaining a good skincare routine, avoiding heavy creams, and staying hydrated.
Conclusion:
Milia, or eyelid bumps, are a common skin issue that can be managed with appropriate care and treatment. Understanding their causes, types, risk factors, and available treatments can help in addressing and preventing these bumps effectively. For persistent or severe cases, consulting a dermatologist is recommended for tailored treatment and guidance.
Read More:



